Cash Reserve Ratio
Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) is defined as the share of a financial institution’s overall deposit which is mandated by the RBI or the Reserve Bank of India to be kept with the RBI as reserves of liquid cash. It is the minimal percentage/proportion of a financial institution’s deposits to be maintained in the form of cash.

Role of Cash Reserve Ratio
CRR plays a crucial role as a reference rate when finding out the base amount/base rate. This base amount is the minimum lending rate & banks are not allowed to lend funds at a rate lower than that. The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is responsible for determining this base rate.
The base rate makes sure of lucidity w.r.t lending and borrowing in the credit market and it is fixed. This rate aids the banks to be able to extend affordable loans by cutting down their cost of lending. Also, there are 2 major objectives of Cash Reserve Ratio:
- Cash Reserve Ratio or CRR makes sure that a portion of the financial institution’s deposit remains with the Central Bank & is thus, secure.
- One other objective of the cash reserve ratio is keeping inflation under proper control. When there is high inflation in the economy, the Reserve Bank of India raises the cash reserve ratio to decrease the amount of cash left with banks in order to sanction loans. It squeezes the cash flow in the economy, getting down inflation by reducing investments.
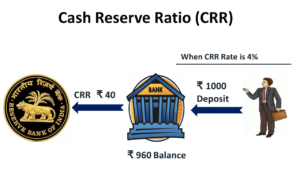
How does Cash Reserve Ratio work?
The amount of cash available to the banks decreases when the RBI decides to inflate the Cash Reserve Ratio. In his way, RBI manages to control the excess flow of money in our economies. The amount of balance that should be maintained by banks with the Reserve Bank of India is not meant to be lower than 4 per cent out of the total Net Demand and Time Liabilities (NDTL). This rate is updated after every two weeks.
The term ‘NDTL’ is the total net demand and time liabilities or deposits that are kept by the banks. It involves deposits from the public (general) & the balances that are held by a bank with other banks. Demand deposit comprises all liabilities that the financial institution is required to pay on demand (for example, balances in overdue fixed deposits, demand drafts, current deposits, and demand liabilities part of savings account deposits).
Time deposits are comprised of deposits that are required to be re-paid on achieving maturity & where the depositor can not take out cash immediately. On the other hand, they have to wait for a certain period of time to get access to the funds (which includes staff security deposits, time liabilities part of savings deposits and fixed deposits). The bank liabilities involve investment in deposits in other banks, certificates of deposit and call money loans.
In what way does Cash Reserve Ratio affect the economy?
Cash Reserve Ratio or CRR is one of the major aspects of the Reserve Bank of India’s monetary policy, that’s applied in order to moderate the cash supply, liquidity & inflation level in our country. The liquidity with the banks goes lower as the CRR goes higher & vice-versa. When there are high levels of inflation, they try to lower the flow of cash in the economy.
RBI helps lower the loanable funding in banks by increasing the cash reserve ratio. All this impedes the money supply in our economy by slowing down investments. This in turn puts down the inflation curve.
However, the RBI lowers the CRR when it wishes to supply funding into the economy, which upscales the loanable funding in banks. In return, the banks sanction a huge quantity of loan deals to industries & businesses for various investment reasons. The growth rate of the economy increases as a result of the increase in the overall supply of money due to this.
Cash Reserve Ratio Vs Statutory Liquidity Ratio
The most important components of the monetary policy include both CRR and SLR. However, there sure exist a few differences between the two of these. You can refer the following table in order to know more about the dissimilarities between the two:
| Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR) | Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) |
| For SLR, financial institutions are expected to possess reserves of liquid assets, which include government securities, gold & cash. | For CRR, financial institutions are expected to possess only cash reserves with the RBI |
| Banks earn returns on money parked as SLR | Banks do not earn returns on money parked as CRR |
| It is used to regulate the financial institution’s leverage for credit expansion. | The Central Bank manages & regulates the liquidity inside the banking system through CRR |
| The securities are held with the banks only in case of SLRs. These are securities they need to maintain as liquid assets. | The money reserve is managed by the banks with the Reserve Bank of India in the case of CRR. |
Why is Cash Reserve Ratio changed regularly?
According to the guidelines laid down by the Reserve Bank of India, all banks are required to keep up a ratio of their total deposits that can also be held with RBI depositories. The Reserve Bank of India is allowed to change the ratio at regular intervals from time to time. A minor change in the ratio affects the economy. Profits are made by lending in the case of the banks. Banks may lend out maximum loan amounts in order to achieve this goal so as to ensure bigger profits and possess little money with them. If ever the customers unexpectedly ask for the withdrawal of their deposits, banks will not be able to cope with the re-payment requirements.
In order to make sure that there is always a certain portion of every deposit in all banks kept safe in their possession, Cash Reserve Ratio is very integral. We know that ensuring liquidity against deposits is the major priority of the cash reserve ratio, but it also takes an equally active part in controlling the rates of interest in the economy. By adjusting the percentage of liquidity available in the system, the Reserve Bank of India ensures the short-term volatility in these interests. A more than needed money in the economy will lead to the government body to surely increase interest rates so as to decrease inflation.
FAQs about Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR)
✅ Why is it important to know my CRR?
Therefore, if you’re a depositor, it is imperative for you to be aware of the current cash reserve ratio in the economic market. By doing this, you ensure that a certain amount of your money is safe with RBI even if there’s a decline in your bank’s performance.
✅ How is CRR related to bank performance?
The higher the Cash Reserve Ratio, the lesser is the amount of money available to banks for lending and investing.
✅ What is the percentage of cash reserve ratio?
This percentage is fixed by the RBI and gets moderated after certain intervals by the government body itself. Currently, the Cash Reserve Ratio is fixed at 3%.




